Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1
|
Vasco da Gama’s discovery of a route to India by sea proved to be
A | very profitable, since da Gama returned with a cargo of spices and made a profit of
several thousand percent. | B | far too costly to be sailed on a regular
basis. | C | the only time any Portuguese vessel sailed the route. | D | much longer than the
route to India by land. |
|
|
|
2
|
What was the name of the set of principles that dominated economic thought in
the seventeenth century?
A | commercial capitalism | C | speculation | B | consumerism | D | mercantilism |
|
|
|
3
|
What is the correct list of social classes from colonial Latin America?
A | missionaries, viziers, mestizos, Native Americans | B | peninsulares,
creoles, mestizos, mulattoes | C | Native Americans, mestizos, peninsulares,
viceroys | D | kings, viceroys, Native Americans, missionaries |
|
|
|
4
|
Sixteenth-century Spanish colonial holdings in America included all of the
following EXCEPT
A | Cuba. | C | Brazil. | B | Peru. | D | Mexico. |
|
|
|
5
|
The Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in 1494,
A | put an end to the war between Portugal and Spain. | B | established a line of
demarcation between territories controlled by Portugal and those controlled by
Spain. | C | ended the violence between Portuguese and Muslim traders. | D | made Portuguese the
official language of the Americas. |
|
|
|
6
|
According to mercantilists, the prosperity of a nation depended on
A | a large supply of bullion, or gold and silver. | B | an effective
ruler. | C | conquering new territories and expanding the nation’s intellectual
resources. | D | finding and maintaining a supply of cheap labor, preferably
slaves. |
|
|
|
7
|
What was the name for the journey of enslaved persons from Africa to
America?
A | the Voyage of Sorrow | C | the Atlantic Journey | B | the Bering Crossing | D | the Middle
Passage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8
|
 What nation sponsored the first successful
circumnavigation of the globe? A | Portugal | C | France | B | England | D | Spain |
|
|
|
9
|
 How many years did it take Sir Francis Drake to
circumnavigate the world? A | 13 years | C | 3 years | B | 10 years | D | 5 years |
|
|
|
| The different ways in which the Spanish, French, and English explored
and colonized the Americas reflect their differing perceptions of the regions. Spanish explorers were
enticed to search for legendary cities such as El Dorado, where the streets were said to be paved
with gold, and the Seven Cities of Cibola, which allegedly held enormous treasures . . . French
explorers, however, looked at North America as a place where fortunes could be made from the fur
trade. Settlements were temporary hunting communities, quite different from English farming colonies,
where families have migrated to start a new life in a new land. | |
|
|
|
10
|
 What was the difference between French and English
settlements? A | French settlements were temporary. | B | French settlements consisted of large family
groups. | C | French settlements supported explorers looking for treasures. | D | French settlements
were always surrounded by farm land. |
|
|
|
11
|
Philip II of Spain was known as the
A | “Huguenot King.” | C | “King of the Holy Roman
Empire.” | B | “Most Catholic King.” | D | “Papal
King.” |
|
|
|
12
|
James I of England believed in the divine right of kings, which is
A | the belief that a king was granted the wisdom of God upon ascending to the throne,
and therefore was faultless. | B | the concept that kings were equal to God, and
therefore did not have to live by the laws of the Church. | C | the theory that kings
alone could know the mind of God, and therefore could determine the future through
divination. | D | the idea that kings receive their power from God and are responsible only to
God. |
|
|
|
13
|
The foundation for a constitutional monarchy in England was laid by the
A | Toleration Act of 1489. | C | English Civil War. | B | Bill of Rights. | D | Rump Parliament. |
|
|
|
14
|
Absolutism is
A | the practice by monarchs of undergoing daily absolution to keep states free of the
burden of sin. | B | the belief that all citizens within a state must conform to one
religion. | C | an offshoot of Islam, in which it is believed that baptism absolves all past and
future sins. | D | a system of government in which a ruler holds total
power. |
|
|
|
15
|
Louis XIV maintained complete authority as monarch by
A | executing the previous monarch’s entire family. | B | maintaining a network
of spies to find conspirators against him. | C | distracting the nobles and royal princes with
court life, to keep them out of politics. | D | bestowing lavish riches on any serf who
supported his right to rule. |
|
|
|
16
|
The Edict of Nantes recognized Catholicism as the official religion of France,
and
A | gave the Huguenots the right to worship and to enjoy all political
privileges. | B | was intended to bring about an end to the battles between the Catholics and the
Spanish, but actually only served to inflame tensions. | C | declared all Huguenots to be enemies of the
state. | D | was largely ignored by the Huguenots, and served only to appease the
pope. |
|
|
|
“The Queen has reigned already
twenty-six years, and during her reign Parliament has never been held. This year she enters her
fifty-third year, as it is said, and she has sent orders through the whole realm to convoke
Parliament. The principal cause is, I am told, that the English do not wish the King of Scotland, who
is the next to the throne, to be King of England, and wish to know who after the queen’s death
is to wear the crown. I have forgotten the exact date, but I believe the opening of Parliament took
place on November 25th.”
—Leopold von Wedel, 1584 | |
|
|
|
17
|
 According to this passage, why did Queen Elizabeth
order Parliament to meet? A | to discuss the next heir to the throne | B | to discuss financial matters | C | to discuss plans for
war | D | to discuss a recently passed law |
|
|
|
18
|
 According to this passage, what had never happened
during Queen Elizabeth’s twenty-six year reign? A | The members of Parliament had never gathered. | B | England had never
gone to war. | C | Laws had never been passed. | D | Treaties had never been
signed. |
|
|
|
19
|
The term ____ is another name for a republic.
A | nation | C | commonwealth | B | democracy | D | monarchy |
|
|
|
20
|
In 1689, what laid the foundation for a limited, or constitutional, monarchy in
England?
A | the Edict of Nantes | C | the Bill of Rights | B | the Toleration Act | D | the Stamp Act |
|
|
|
21
|
John Locke’s ideas suggest that people were
A | born either good or evil. | B | inherently self-centered. | C | naturally inclined to
be stupid. | D | molded by their experiences. |
|
|
|
22
|
To Voltaire and many other philosophers, the universe was
A | a divine creation. | C | like a clock. | B | unknowable. | D | constructed like a
flower. |
|
|
|
23
|
In Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s concept of a social contract,
A | an entire society agrees to be governed by its general will. | B | punishments are not
exercises in brutality, and capital punishment is discarded. | C | the government should
not interfere in economic matters. | D | women should be granted rights nearly equal to
those of men. |
|
|
|
24
|
Montesquieu’s most lasting contribution to political thought was
his
A | analysis of the governmental system of checks and balances. | B | identification of the
natural laws that governed human society. | C | theory that the government should interfere with
religious matters. | D | idea that punishments should be brutal to be
effective. |
|
|
|
25
|
Adam Smith believed in laissez-faire, by which he meant that
A | the assets of the rich should be taken. | B | the state should not
regulate the economy. | C | those who are able to work should help to
support those who cannot work. | D | the state should monitor the economy and impose
regulations to keep it healthy. |
|
|
|
“Let us then suppose the mind to be, as we say, white paper, void
of all characters, without any ideas. How comes it to be furnished? Whence has it all the materials
of reason and knowledge? To this I answer, in one word, from experience . . . . Our observation,
employed either about external sensible objects or about the internal operations of our minds
perceived and reflected on by ourselves, is that which supplies our understanding with all the
materials of thinking.”
—John Locke, “Essay Concerning Human
Understanding” | |
|
|
|
26
|
 According to the passage, how does the mind acquire
knowledge? A | other people | C | God | B | nature | D | experience |
|
|
|
Ptolemaic
Universe
Copernican Universe 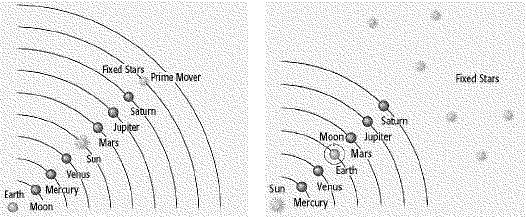
|
|
|
27
|
 What is the most important difference between the
Ptolemaic system and the Copernican system? A | the position of fixed stars | B | the celestial body at the center of the
universe | C | the position of the moon | D | the position of
Jupiter |
|
|
|
28
|
A systematic procedure for collecting and analyzing evidence is known as the
_____ method.
A | inductive | C | rational | B | scientific | D | gravitational |
|
|
|
|
|
|
29
|
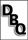 What was unique about the people of the Third
Estate? A | They were the minority. | C | They paid taxes. | B | They owned land. | D | They were very
religious. |
|
|
|
30
|
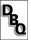 What percentage of land was owned by the
clergy?
|
|
|
31
|
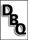 What percentage of the population was
nobility?
|
|
|
“. . . [Louis
XVI] looked at the scaffold without flinching. The executioner at once proceeded to perform the
customary rite by cutting off the King's hair, which he put in his pocket. Louis then walked up
onto the scaffold. The air was filled with the roll of numerous drums ... with such force that
Louis's voice was drowned and it was only possible to catch a few stray words like 'I
forgive my enemies'...."
— From a letter by Philipe Pinel,
physician
|
|
|
32
|
 French revolutionaries used the guillotine to execute
King Louis XVI because they believed that it A | was the execution method supported by the Third Estate. | B | gave victims a second
chance. | C | killed humanely. | D | could be operated
inexpensively. |
|
|
|
33
|
The French National Assembly swore the Tennis Court Oath, which was
A | a promise to redistribute all the wealth in France. | B | a vow to continue to
meet until they had produced a French constitution. | C | an oath of loyalty to Jean-Baptiste Colbert, an
outspoken lawyer that called for doing away with the relics of feudalism. | D | a promise not to rest
until all members of the clergy were tried and executed. |
|
|
|
34
|
In his final battle, Napoleon was defeated by
A | the bitter Russian winter. | B | a combined French and Swiss
army. | C | a combined British and Prussian army. | D | the superior British
navy. |
|
|
|
35
|
The Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen proclaimed
A | equal rights for all men, but no political rights for women. | B | an end to the
monarchy and the abolishing of a National Assembly. | C | equal rights for all citizens, including equal
political rights for women. | D | an end to the National police
force. |
|
|
|
36
|
The most important of the seven legal codes established by Napoleon was
A | the Religious Code. | C | the Merchant Code. | B | the Foreign Policy Code. | D | the Civil Code. |
|
|
|
37
|
Promotion within Napoleon’s new bureaucracy was
A | based on location. | B | given to those Napoleon favored, but taken away
as soon as they fell out of favor. | C | based on ability only, not rank or
birth. | D | designed to benefit the nobility and keep the middle class from obtaining
high-ranking positions. |
|
|
|
Law is the expression of the general will; all citizens have the right
to concur personally, or through their representatives, in its formation; it must be the same for
all, whether it protects or punishes. All citizens, being equal before it, are equally admissible to
all public offices, positions, and employments, according to their capacity, and without other
distinction than that of virtues and talents.
—Declaration of the Rights of
Man and of the Citizen, French National Assembly, 1789 | |
|
|
|
38
|
 How, according to the passage, is law an expression
of the general will? A | The king, as the people’s leader, defines the law. | B | The nobles ensure
that the law meets the needs of all people. | C | Old laws are changed to meet new
needs. | D | All citizens are able to influence the law’s
creation. |
|
|
|
39
|
 According to the passage, are all citizens given
public office? A | Yes; all citizens are equal and given public office. | B | No; only 50 percent
of the citizenry are given public office. | C | No; all citizens are equal, but some with more
talent and skill earn public office. | D | Yes, but only if they pay for access to the
public office. |
|
|
|
40
|
To ensure loyalty, who did Napoleon install on the thrones of the lands he
conquered?
A | his relatives | B | Directory | C | consulate | D | Duke of
Wellington |
|
|
|
41
|
What were some of the most important causes of the French Revolution?
A | Protestant Reformation, storming of the Bastille, financial
crisis | B | Enlightenment ideas, war with Russia, rise of Napoleon | C | Protestant
Reformation, storming of the Bastille, Third Estate | D | Enlightenment ideas, rigid social structure,
financial crisis |
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
42
|
Napoleon’s downfall began in 1812 when he decided to invade
_____________________.
|
|
|
43
|
Napoleon’s establishment of the _____________________ was a step backward
for the rights of women and children.
|
|
|
44
|
________ is the sense of unique identity of a people based on common language,
religion, and national symbols.
|
Essay
|
|
|
45
|
Describe the impact of the Peace of Westphalia on Germany and the Holy Roman
Empire.
|
|
|
46
|
Describe how nationalism unified the people in countries that Napoleon
invaded.
|